CLEAR WINES
2024
WHAT IS A CLEAR WINE?
[EXPLANATION]

THE GRAPES
[THE 3 GRAPES]
To make Champagne, you have to start by making wine, which is virtually white.
Our first singularity = white wine production is based on white grape varieties, but for the most part on black grape varieties.
The 3 main Champenois grape varieties are :
- Chardonnay: a white grape variety (white skin and white juice)
- Pinot Noir: a black grape variety (black skin and white juice)
- Pinot Meunier: a black grape variety (black skin and white juice)
PRESSING
[CHAMPENOIS]
To obtain a white juice from black grape varieties, there are several steps to follow during pressing:
- Pressing as soon as the grapes are picked
- Press whole bunches (not crushed)
- Gentle, progressive, fractional pressing
- Fractionate* the juice as it leaves the press.
*Fractionation consists of separating the juice from the first press, known locally as the "CUVÉE", and the juice from the second press/end of press, known locally as the "TAILLE".

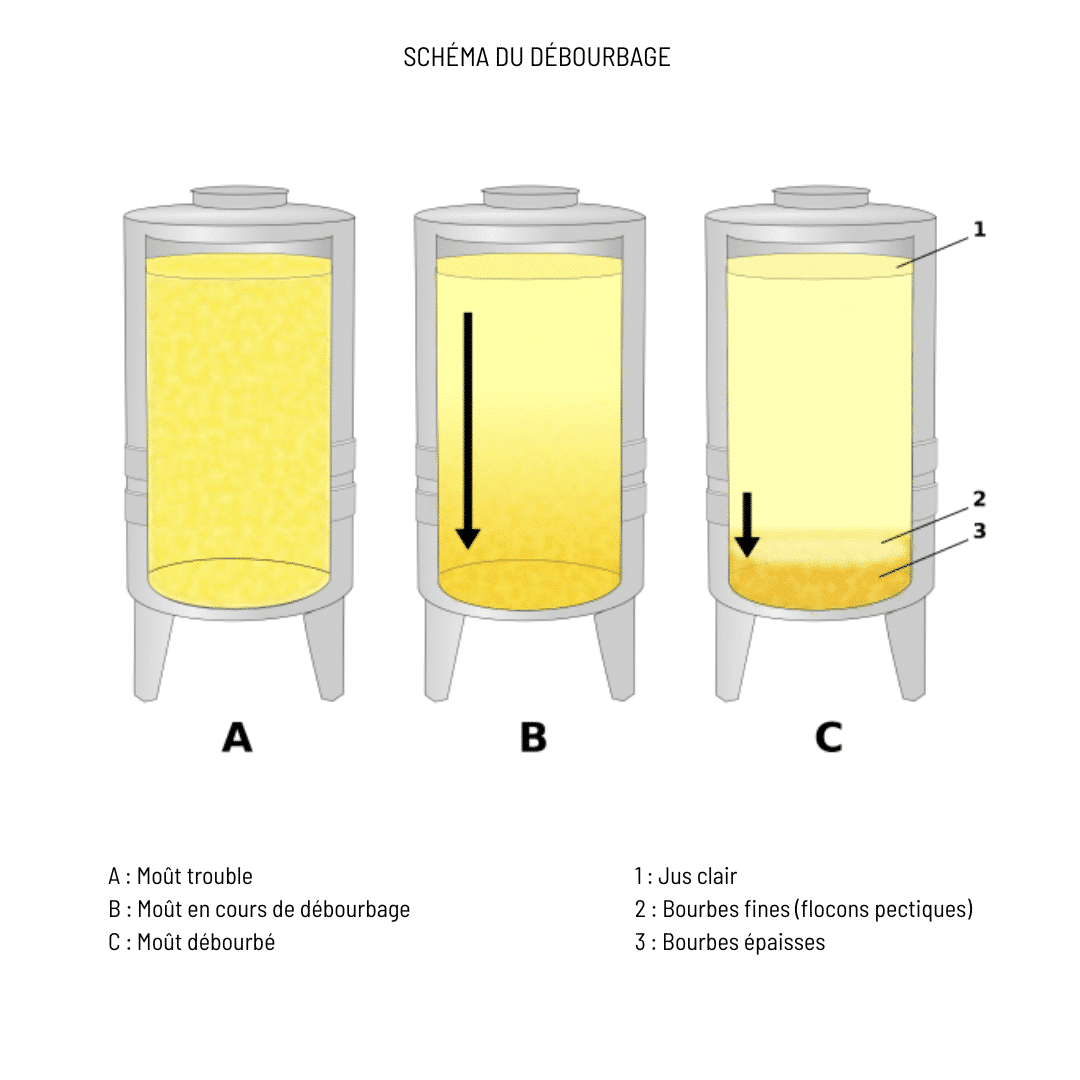
LE DÉBOURBAGE
[REMOVE IMPURITIES]
The juice we call "must", extracted from the press, is then stored in vats, depending on the grape variety and parcel of origin.
After a period of 12 to 24 hours, the impurities (stalks, berry skins, pips) known as "bourbes" settle to the bottom of the vat.
The musts are then pumped into the tank, where they are pumped off.
The musts are then pumped to our fermentation tanks.
FERMENTATION
[ALCOHOLIC]
The musts then undergo a fermentation process.
The first fermentation is called Alcoholic Fermentation. This transforms the must into wine.
What is Fermentation?
Sugars + Yeast = Alcohol + CO2
In concrete terms, yeast "eats" the sugar, producing alcohol and carbon dioxide.


CLARIFICATION
[WINE CLARIFICATION]
After fermentation, the wine is left to rest for a few months for clarification.
Free of solid particles, these basic wines are now known as "vins clairs".
Still classified by grape variety, year, crus or even parcel, cuvée wines, size wines, they are ready for blending.